Prof. Dr. Serbülent Gökhan Beyaz
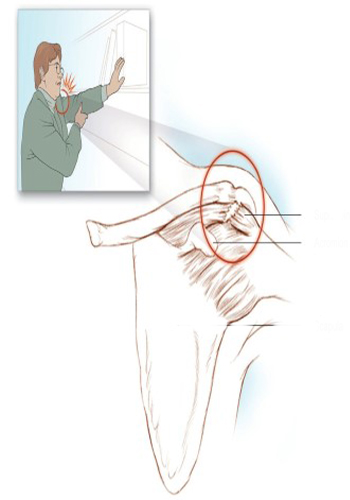
Rotator Cuff Tear
Rotator Cuff Tear
Rotator Cuff tears are a common cause of shoulder pain and shoulder dysfunction or shoulder dysfunction. November of the Rotator Cuff (cuff), usually a minor trauma to the muscles and tendons of the shoulder then it develops. However, the pathological process responsible for tearing occurs as a result of a prolonged and persistent inflammation of the tendon (tendonitis). Rotator Cuff (cuff) supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, teres minor november consists of november and tendons of these muscles. The Rotator Cuff november in conjunction with other muscles, tendons and ligaments of the shoulder to rotate the arm and help provide stability along the shoulder joint. In addition to pain october, patients suffering from rotator cuff rupture usually experience a gradual decrease in functional abilities. Even daily simple tasks, such as combing hair, tying a bra, become quite difficult, as the shoulder range of motion decreases. If there is no improvement and treatment is delayed, november weakness and dull shoulder (not moving the shoulder at all) may develop due to less use of the shoulder joint, after constant use.
Signs and Symptoms
Rotator patients admitted with a cuff tear are often unable to lift the affected arm above shoulder level without using their intact arm. On physical examination, the infraspinatus was affected if there was weakness in the external rotation. Shoulder if there is weakness in the abduction above its level, the supraspinatus is affected. Sensitivity is often present with palpation in the subacromial region. Patients with a partial rotator cuff tear lift the arm above the head level he loses his ability. Patients with complete rupture completely lose the ability to lie down above shoulder level, as well as the displacement of the anterior humeral head. The pain of the rotator cuff tear is constant and severe. Also it is exacerbated by abduction and external rotation of the shoulder. Sleep disturbance is often reported due to pain. Patients are advised to try to keep the inflamed subscapularis tendon stable by limiting the medial rotation of the humerus tries. December december rotator cuff tear, the passive range of motion is normal, but the active range of motion is limited; in the dull shoulder, both the passive range of motion and the active december of motion are limited. Rotator cuff rupture over the age of 40 it is rarely observed under it, except in cases of severe trauma.
Treatment
The initial treatment includes a combination of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, as well as physical therapy. Regional hot and cold applications can be useful. The response to these treatments for patients who do not give, the injection techniques that will be described here can be applied as a previous step before surgery. These injections have been done with the help of fluoroscopy in recent years, and now with the help of ultrasound these injections are administered. Simultaneous observation of the place to be applied is very helpful both in terms of diagnosis and verification of the place where the injection was made. Since fluoroscopy shows bone structures in one dimension most often it is useful to perform joint injections (acromioclavicular and glenohumeral joint). Whereas Ultrasonography is not only joint injections, but also its structure is broken, full fold or partial tear it allows injections by diagnosing november muscles and tendons simultaneously and quite successful results are obtained. Physical methods, including regional heat application and light range-of-motion exercises, provide the patient with it should be applied a few days after the injection is made. Severe exercises should be avoided, as this will aggravate the patient’s symptoms and can lead to a complete tendon rupture.