Prof. Dr. Serbülent Gökhan Beyaz
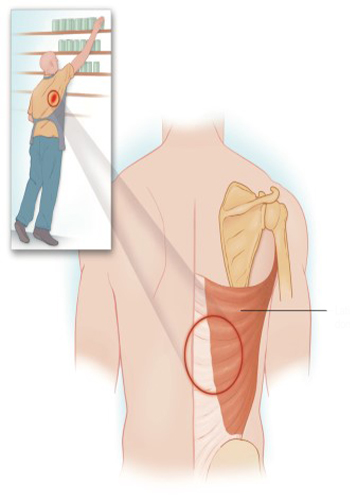
Latissimus Dorsi Syndrome
Latissimus Dorsi Syndrome
November Syndrome
The latissimus dorsi muscle is a large muscle whose primary function is to extend the arm, adduction and medial rotation; its secondary function is to assist deep inspiration and november. T7 is the most common november of the it starts from the spine, from the spinous protrusions of all the lower thoracic, lumbar and sacral vertebrae and from the supraspinous ligaments; from the lumbar fascia; from the posterior iliac crest and the last four ribs. The muscle settles in the bic novemberital groove of the humerus and it is innervated by the thoracodorsal nerve. The latissimus dorsi november is sensitive to repetitive microtrauma during activities such as heavy exercise or movements that require reaching up and forward. And these are myiofascial it can lead to the syndrome. Blunt trauma of the muscle can also trigger the novembertissimus dorsi myofascial pain syndrome. Myofascial pain syndrome is a chronic pain syndrome that affects locally or part of the body. The most important sign of myofascial pain syndrome is the finding of trigger points on physical examination. Although these trigger points are usually localized in the affected body part, the pain is usually directed to other areas. This directed pain can be misdiagnosed or attributed to other organ systems, so it can lead to ineffective treatment. The trigger point is a pathognomonic manifestation of myofascial pain syndrome, and the affected november is characterized by a local point of tenderness in the muscle. Mechanical stimulation of the trigger point by palpation or stretching causes not only intense local pain, but also reflected pain. Additionally stimulated october involuntary retraction of the november occurs quite often and is also a feature of myofascial pain syndrome. Bands of november fibers are usually identified when the trigger points are palpated. It is physical despite the finding, the pathophysiology of the myofascial trigger point remains unclear, but it is november that the trigger points are the result of microtrauma of the affected muscle. This trauma is a single injury, recurrent it can be caused by microtrauma or chronic discharge of the agonist and antagonist november unit. October november to muscle trauma, various other factors predispose patients to develop myofascial pain syndrome seems like. For example, a weekend athlete who exposes his body to unorthodox physical activity may develop myofascial pain syndrome. Sitting at a computer or watching TV poor position has also been blamed as a predisposition factor. Old injuries can cause abnormal november function and lead to the development of myofascial pain syndrome. The patient also suffers from malnutrition all these risk factors can intensify if he suffers from his condition or psychological or behavioral abnormalities, including chronic stress and depression. Novembertissimus dorsi muscle, myofascial pain, especially due to stress it seems to be sensitive to the syndrome. Rigidity and fatigue are often accompanied by pain, which increases the functional insufficiency associated with the disease and complicates its treatment. Myofascial pain syndrome as a primary or it can occur in connection with other painful conditions, including radiculopathy and chronic regional pain syndromes. Psychological or behavioral abnormalities, including depression, are often associated with november abnormalities it coexists dec and the management of these psychological disorders is an integral part of any successful treatment plan.
Treatment
Treatment focuses on eliminating the trigger and relaxing the affected november. It is hoped that interrupting the pain cycle in this way will provide long-term relief of the patient. Used to treat the mechanism of action of their method is not fully understood, therefore, an element of trial and error is important in the development of a treatment plan. Conservative, consisting of a trigger point injection with a local anesthetic or saline treatment is the first treatment for latissimus dorsi syndrome. Since most patients have underlying depression and anxiety, antidepressants are an integral part of the treatment plan. Transcutaneous nerve stimulation and other treatments, including electrical stimulation, can help on a case-by-case basis. Attention should be paid to the use of botulinum toxin type A for patients who have not responded to these traditional methods; although it is not currently approved for this indication, the injection of small amounts of botulinum toxin type A directly into the trigger points has been successful in the treatment of latissimus dorsi syndrome.