Prof. Dr. Serbülent Gökhan Beyaz
Neck Muscle Strain
Neck Muscle Strain
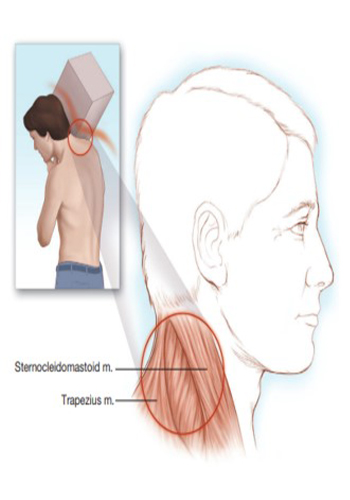
Acute Neck Muscle Strain is a set of symptoms often accompanied by headache, which is not radicular, spreading non-dermatomaly to the shoulders and the area between the two scapulae. With muscle spasm and limited range of motion of the cervical spine, the trapezius muscle is often affected. Neck strain is usually the result of trauma to the cervical spine and associated soft tissues, but is an obvious trigger. can occur without incident. Pathological lesions responsible for this clinical syndrome may originate from soft tissues, facet joints or intervertebral discs.
Signs and Symptoms
Neck pain, cervical is the hallmark of the strain. It may start in the occipital region and spread non-dermatomaly to the shoulders and interscapular region. The pain of cervical strain is usually associated with movement of the cervical spine and shoulders. intensifies. Headaches often occur and can be worsened by emotional stress. Difficulty concentrating on simple tasks and trouble sleeping are also common. Depression can occur with long-term symptoms. On physical examination tenderness appears on palpation; Paraspinous muscle and trapezius spasm are often present. Decreased range of motion is almost always present, and pain increases when this maneuver is attempted. Frequent complaints of pain in the upper extremity Despite this, the neurological examination of the upper extremity is within normal limits.
Treatment
Tension due to cervical muscle strain is best treated with a multimodality approach. Physical therapy including heat modalities and deep massage and combined treatments including NSAIDs and muscle relaxants are for the beginning. suitable. For symptomatic relief, cervical epidural block, blocking of the medial branch of the dorsal ramus or intra-articular injection of the facet joint with local anesthetic and steroid are extremely effective. underlying sleep disorder and depression are treated with a tricyclic antidepressant such as nortriptyline, which can be started with a single 25 mg dose at bedtime. Cervical facet block is usually combined with atlanto-occipital block when treating pain in this area. are combined. Although the atlantooccipital joint is not a true facet joint in the anatomical sense, the atlanto-occipital block is similar to the facet joint block commonly used by professionals working in the pain field and thus visible.