Prof. Dr. Serbülent Gökhan Beyaz
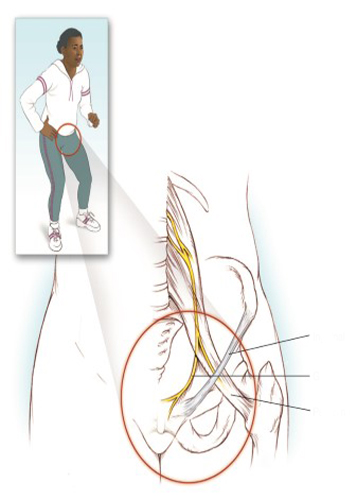
Genitofemoral Neuralgia
Genitofemoral Neuralgia
Clinical Syndrome
Genitofemoral neuralgia is one of the most common conditions of lower abdominal and pelvic pain. Damage may occur due to compression of the genitofemoral nerve. The most common cause of genitofemoral neuralgia is traumatic damage to the nerve, it is a blunt trauma and inguinal herniophagy, as well as pelvic surgery. It can also be seen as spontaneous.
Genitofemoral neuralgia is characterized by paresthesia, burning-like pain, and often numbness in the lower abdomen radiating to the inner thigh; it spreads to the lower and cremaster november, the labia major in the woman; the pain does not spread below the knee. Genitofemoral neuralgia can worsen with lumbar extension due to stretching of the nerve. However, patients are often inclined forward, novice they stand in the position of skiers. On physical examination, sensory loss is observed in the inner thigh, the base of the scrotum and the labia major. Weakness of the anterior abdominal wall can be traced. The Tinel sign is visible.
Treatment
Treatment of genitofemoral neuralgia can be provided with analgesics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and COX-2 inhibitors. Repetitive activities can aggravate the pain. Pharmacological treatment is usually not very effective however, an ilioinguinal nerve block performed using local anesthetics and steroids is necessary.